You are welcome to this blog. Dear friends if you need help about any topic, you are free to write your query in comment box.I will do my best to help you.
Thursday, 30 May 2013
Trigonometric functions of an acute angle (All Mathematical Formulae) --By: Vinod Kumar Dhundhara
Trigonometric functions of an acute angle
Trigonometric functions of an acute angle are ratios of different pairs of sides of a right-angled triangle
( Fig. )
1) Sine: sin A = a / c ( a ratio of an opposite leg o a hypotenuse ) .
2) Cosine: cos A = b / c ( a ratio of an adjacent leg to a hypotenuse ) .
3) Tangent: tan A = a / b ( a ratio of an opposite leg to an adjacent leg ) .
4) Cotangent: cot A = b / a ( a ratio of an adjacent leg to an opposite leg ) .
5) Secant: sec A = c / b ( a ratio of a hypotenuse to an adjacent leg ) .
6) Cosecant: cosec A = c / a ( a ratio of a hypotenuse to an opposite leg ) .
There are analogous formulas for another acute angle B ( Write them, please ! ).
E x a m p l e . A right-angled triangle ABC ( Fig.2 ) has the following legs:
a = 4, b = 3. Find sine, cosine and tangent of angle A.
a = 4, b = 3. Find sine, cosine and tangent of angle A.
S o l u t i o n . At first we find a hypotenuse, using Pythagorean theorem:
c 2 = a 2 + b 2,
According to
the above mentioned formulas we have:
sin A = a / c = 4 / 5; cos A = b / c = 3 / 5; tan A = a / b = 4 / 3.
sin A = a / c = 4 / 5; cos A = b / c = 3 / 5; tan A = a / b = 4 / 3.
For some angles it is possible to write exact values
of their trigonometric functions. The most important cases are presented
in the table:
Although angles 0°
and 90° cannot be acute in a right-angled triangle, but at enlargement
of notion of trigonometric functions ( see below), also these angles
are considered. A symbol 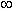 in the table means that absolute value of the function
increases unboundedly, if the angle approaches the shown value.
in the table means that absolute value of the function
increases unboundedly, if the angle approaches the shown value.
Formulas of abridged multiplication (All Mathematical Formulae) --By: Vinod Kumar Dhundhara
Formulas of abridged multiplication
From the rules of multiplication of sums and
polynomials the following seven formulas of abridged multiplication can
be easily received. It is necessary
to know them by heart, as they are used in most of problems in mathematics.
[1] ( a + b )²
= a² + 2ab + b² ,
[2] ( a – b )²
= a² – 2ab + b²
,
[3] ( a + b ) ( a – b ) = a²
– b²,
[4] ( a + b )³
= a³
+ 3a² b + 3ab²
+ b³ ,
[5] ( a – b )³
= a ³
– 3a² b + 3ab²
– b³ ,
[6] ( a + b )( a²
– ab + b²
) = a³ + b³ ,
[7] ( a – b )( a ²
+ ab + b²
) = a³ – b³
.
E x a m p l e : Calculate 99³ using the formula [5] .
S o l u t i o n : 99³ = (100 – 1)³ = 1000000 – 3 ·10000 ·1 + 3 ·100 ·1 – 1 = 970299.
S o l u t i o n : 99³ = (100 – 1)³ = 1000000 – 3 ·10000 ·1 + 3 ·100 ·1 – 1 = 970299.
Divisibility criteria (All Mathematical Formulae) --By: Vinod Kumar Dhundhara
Divisibility criteria
Divisibility by 2. A number is divisible by 2, if its last digit is 0 or is divisible by 2. Numbers, which are divisible by 2 are called
even numbers. Otherwise, numbers are called odd numbers.
Divisibility by 4. A number is divisible by 4, if its two last digits are zeros or they make a two-digit number, which is
divisible by 4.
Divisibility by 8. A number is divisible by 8, if its three last digits are zeros or they make a three-digit number, which is
divisible by 8.
Divisibility by 3 and by 9 . A number is divisible by 3, if a sum of its digits is divisible by 3. A number is divisible by 9,
if a sum of its digits is divisible by 9.
Divisibility by 6. A number is divisible by 6, if it is divisible by 2 and by 3.
Divisibility by 5. A number is divisible by 5, if its last digit is 0 or 5.
Divisibility by 25. A number is divisible by 25, if its two last digits are zeros or they make a number, which is divisible by
25.
Divisibility by 10. A number is divisible by 10, if its last digit is 0.
Divisibility by 100. A number is divisible by 100, if its two last digits are zeros.
Divisibility by 1000. A number is divisible by 1000, if its three last digits are zeros.
Divisibility by 11. A number is divisible by 11 if and only if a sum of its digits, located on even places is
equal to a sum of its digits, located on odd places, OR these sums are differed by a number, which is divisible by 11.
There are criteria of divisibility for some other
numbers, but these criteria are more difficult and not considered in a
secondary school program.
| E x a m p l e . | A number 378015 is divisible by 3, because a sum of its digits 3 + 7 + 8 + 0 + 1 + 5 = 24, which is divisible by 3. This number is divisible by 5, because its last digit is 5. At last, this number is divisible by 11, because a sum of even digits: 7 + 0 + 5 =12 and a sum of odd digits: 3 + 8 + 1 = 12 are equal. But this number isn’t divisible by 2, 4, 6, 8, 9, 10, 25, 100 and 1000, because … Check these cases yourself ! |
Laws of addition and multiplication (All Mathematical Formulae) --By: Vinod Kumar Dhundhara
Laws of addition and multiplication
Commutative law of addition: m + n = n + m . A sum isn’t changed at rearrangement of its addends.
Commutative law of multiplication: m · n = n · m . A product isn’t changed at rearrangement of its factors.
Associative law of addition: ( m + n ) + k = m + ( n + k ) = m + n + k . A sum doesn’t depend on grouping of its addends.
Associative law of multiplication: ( m · n ) · k = m · ( n · k ) = m · n · k . A product doesn’t depend on grouping of its factors.
Distributive law of multiplication over addition: ( m + n ) · k = m · k + n · k . This law expands the rules of operations with brackets (see the previous section).
Order of operations. Brackets (All Mathematical Formulae) --By: Vinod Kumar Dhundhara
Order of operations. Brackets
If brackets are absent, the following order of operations is right:
1) raising to a power and extraction of a root (one after another);
2) multiplication and division (one after another);
3) addition and subtraction (one after another).
If brackets are present, at first all operations inside brackets are executedaccording to the aforesaid order, and then the rest of the operations out of brackets are executed (in the same order).
1) raising to a power and extraction of a root (one after another);
2) multiplication and division (one after another);
3) addition and subtraction (one after another).
If brackets are present, at first all operations inside brackets are executedaccording to the aforesaid order, and then the rest of the operations out of brackets are executed (in the same order).
E x a m p l e . Calculate the next expression:
( 10 + 23 · 3 ) + 43 – ( 16 : 2 – 1 ) · 5 – 150 : 52 .
( 10 + 23 · 3 ) + 43 – ( 16 : 2 – 1 ) · 5 – 150 : 52 .
S o l u t i o n . At first, powers must be calculated and changed by theirs values:
( 10 + 8 · 3 ) + 64 – ( 16 : 2 – 1 ) · 5 – 150 : 25 ;
( 10 + 8 · 3 ) + 64 – ( 16 : 2 – 1 ) · 5 – 150 : 25 ;
after this,
multiplication and division in the brackets and out of
them are executed:
( 10 + 24 ) + 64 – ( 8 – 1 ) · 5 – 6 ;
now, additions and subtractions in the brackets are executed:
34 + 64 – 7 · 5 – 6 ;
finally, after the rest of the multiplication 7 · 5 = 35 we receive:
34 + 64 – 35 – 6 = 57 .
them are executed:
( 10 + 24 ) + 64 – ( 8 – 1 ) · 5 – 6 ;
now, additions and subtractions in the brackets are executed:
34 + 64 – 7 · 5 – 6 ;
finally, after the rest of the multiplication 7 · 5 = 35 we receive:
34 + 64 – 35 – 6 = 57 .
Arithmatical operations (All Mathematical Formulae) --By: Vinod Kumar Dhundhara
Addition – an operation of finding a sum of some numbers:
11 + 6 = 17. Here 11 and 6 – addends, 17 – the sum. If addends are changed by places, a sum is saved
the same: 11 + 6 = 17 and 6 + 11 = 17.
Subtraction – an operation of finding an addend by a sum and another addend:
17 – 6 = 11. Here 17 is a minuend, 6 – a subtrahend, 11 – the difference.
Multiplication. To multiply one number n ( a multiplicand ) by another
m ( a multiplier ) means to repeat a multiplicand n as an addend
m times.
The result of multiplying is called a product. The operation of multiplication is written as: n x m or n ·
m . For example, 12 x 4 = 12 + 12 + 12 + 12 = 48. In our case 12 x 4 = 48 or 12 · 4 =
48. Here 12 is a multiplicand, 4 – a multiplier, 48 – a product. If a multiplicand n and a multiplier
m are changed by places, their product is saved the same: 12 · 4 = 12 + 12 + 12 + 12 = 48 and 4 ·12 = 4 + 4 + 4 +
4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 48. Therefore, a multiplicand and a multiplier are called usually factors or multipliers.
Division – an operation of finding one of factors by a product and another factor:
48 : 4 = 12. Here 48 is a dividend, 4 – a divisor, 12 – the quotient. At dividing integers a quotient can be
not a whole number. Then this quotient can be present as a fraction. If a quotient is a whole number, then it is called that numbers are divisible,
i.e. one number is divided without remainder by another. Otherwise, we have a division with remainder. For example, 23 isn’t divided by 4 ;
this case can be written as: 23 = 5 · 4 + 3. Here 3 is a remainder.
Raising to a power. To raise a number to a whole (second, third, forth, fifth etc.) power means to repeat it as a factor two, three,
four, five and so on. The number, repeated as a factor, is called a base of a power; the quantity of factors is called an index or an exponent
of a power; the result is called a value of a power. A raising to a power is written as:
Here 3 – a base of the power, 5 – an exponent (an index) of the power, 243 – a value of the power.
The second power is called a square, the third one – a cube. The first power of any number is this number.
Extraction of a root – an operation of finding a base of a power by the power and its exponent:
Here 243 – a radicand, 5 – an index (degree) of the root, 3 – a value of the root. The second root is called a square root, the third root – a cube root.The second degree of square root isn’t written:
Addition and subtraction, multiplication and division, raising to a power and extraction of a root are two by two mutually
inverse operations.
Wednesday, 29 May 2013
General science question for RAS RPSC EXAM, General Science Questions & Answers for RAS/RTS --By: Vinod Kumar Dhundhara
General
science question for RAS RPSC EXAM
General
Science Questions & Answers for RAS/RTS
No. Question Answer
01 The theory of relativity was propounded by Albert Einstein
02 The principal metal used in manufacturing steel is Iron
03 An altimeter is used for measuring Altitude
04 Oology is the study of Birds eggs
05 Radioactivity was discovered by Henry Bacquerel
06 The metal used in storage batteries is Lead
07 The instrument used to measure the relative humidity of air is Hygrometer
08 Barometer was invented by Torricelli
09 The unit of power is Watt
10 Radium was discovered by Marie and Pierrie Curie
11 The existence of isotopes was discovered by Frederick Soddy
12 Dynamo was invented by Michael Faraday
13 The nuclear reactor was invented by Enrico Ferni
14 The law of gravitation was propounded by Sir Isaac Newton
15 Crescograph was invented by J.C.Bose
16 Crescograph is used to measure the Rate of growth of a plant
17 Galileo's first scientific discovery was Pendulum
18 Microscope was invented by Aaton Van Leewen Hock
19 The scientist who is known as father of modern biology is Aristotle
20 The first person to see a cell under microscope was Robert Hooke
21 The smallest flowering plant is Worffia
22 The four blood groups were discovered by Karl Landsteiner
23 Sodium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy
24 The atomic number of oxygen is Eight
25 The basic building blocks of proteins are Amino acids
26 The botanical name of the cotton plant is Gossipium Hirsutum
27 An Electroscope is used to Detect charges on a body
28 The unit of loudness is Phon
29 An ammeter is used to measure Electric current
30 Plant that eat insects are called Insectivorous plants
31 Fruits that are formed without fertilization are called Parthenocarpic
32 Plants that flower only once in their lifetime are called Mono carpic
33 The botanical name for rice is Oryza Sativa
34 Penicillin is obtained from Mould
35 The largest tree in the world is Seguoia Gigantica
36 Herpetology is the study of Reptiles
37 Entomology is the study of Insects
38 Ornithology is the study of Birds
39 Ichtyology is the study of Fishes
40 Osteology is the study of Bones
41 The botanical name for brinjal is Solanum melongenal
42 The botanical name for onion is Allium Cepa
43 The study of sound is called Acoustics
44 The study of heavenly bodies is called Astronomy
45 The study of tissues is called Histology
46 Electric Lamp was invented by Thomas alva Edison
47 The fear of crowd is called Ochlophobia
48 The fear of books is called Bibliophobia
49 The fear of going to bed is called Clinophobia
50 The symbol of gold is Au
51 The symbol of sodium is Na
52 The symbol of Sr stands for Strontium
53 The symbol Rb stands for Rubidium
54 The symbol Md stands for Mendelevium
55 Calcium sulphate is commonly called Plaster of Paris
56 Sodium carbonate is commonly called Washing Soda
57 Sodium chloride is commonly known as Common Salt
58 The chemical name of Chloroform is Trichloromethane
59 The chemical name of baking powder is Sodium bicarbonate
60 The chemical name of bleaching powder is Calcium hypochlorite
61 The formula HCL stands for Hydrochloric Acid
62 The formula H2SO4 stands for Sulphuric Acid
63 The formula CHCI3 stands for Trichloromethane
64 The formula H2O2 stands for Hydrogen peroxide
65 A fungus which can only survive on other living organisms is called Obligate Parasite
66 A plant which lives in the dark is called Scotophyte
67 A plant adapted to live in dry places is called a Xerophyte
68 A plant adapted for growth in water is called a Hydrophyte
69 Bifocal lens was invented by Benjamin Franklin
70 Cement was invented by Joseph Aspdin
71 Laser was invented by Dr.Charles H.Townes
72 Electromagnet was invented by William Sturgeon
73 Rayon was invented by Sir Joseph Swann
74 Thermostat is an instrument used for regulating Constant temperature
75 The science of organic forms and structures is known as Morphology
76 Phycology is the study of Algae
77 Tata Institute of Fundamental Research was established in 1945
78 CSIR stands for Council of Scientific and Industrial Research
79 ISRO stands for Indian Space Research Organisation
80 The first human being to land on moon was Neil Armstrong
81 The first Indian in space was Rakesh Sharma
82 ISAC stands for ISRO Satellite Centre
83 VSSC stands for Vikram Sarabhai space Centre
84 The headquarters of ISRO is located at Bangalore
85 VSSC is located at Thiruvananthapuram
86 ISAC is located at Bangalore
87 National Science Centre is located at New Delhi
88 Central Tobacco Research Institute is located at Rajahmundry
89 Indian Institute of Horticultural Research is located at Bangalore
90 The Atomic Energy Commission was set up in August 1948
91 The first Indian Satellite was Aryabhatta
92 The first Indian Satellite was launched in the year 1975
93 ASLV stands for Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle
94 INSAT stands for Indian National Satellite
95 The fear of women is known as Gynophobia
96 The fear of men is known as Androphobia
97 The scientist who developed the Quantum theory was Max Plonck
98 The steam engine was invented by James Watt
99 The botanical name of tea is Camellia Sinensis
100 Logarithms were devised by John Napier
101 The acid used in a car battery is Sulphuric acid
102 The system for writing by blind people was invented by Louis Braille
103 The parachute was used for the first time by J.P.Blanchard
104 The German physicit who first demonstrated the existence of Radio waves was Henrich Hertz
105 The instrument that records the intensity of earthquakes is Seismograph
106 The laws of floating bodies was discovered by Archimedes
107 The density of milk is measured by a Lactometer
108 Fountain pen was invented by L.E.Waterman
109 The instrument used to measure the pressure of gases is the Monometer
110 Bhaskara I was a famous Astronomer
111 The first atomic power station established in India was the Tarapore Atomic Power Station
112 The role of heredity was demonstrated by Mendel
113 The instrument used to measure the concentration of salt water is the Salinometer
114 Spectroscopy is the study of Anders John Angstrom
115 Dactylography is the study of Finger Prints
116 A tangent galvanometer is used to study the Strength of direct current
117 The fruit of Oak is called Acron
118 ZETA stands for Zero Energy Thermonuclear Assembly
119 The formula C6H5OH stands for Phenol
120 Michael Faraday worked as an assistant under another scientist whose name was Sir Humphry Davy
121 Vulcanised rubber was invented by Charles Goodyear
122 The symbol Zn stands for Zinc
123 The symbol He stands for Helium
124 Celluloid was invented by A.Parker
125 Glider was invented by Sir George Caley
126 Safety matches was invented by J.E.Lundstrom
127 Radio valve was invented by Sir J.A.Fleming
128 Space Applications Centre is located at Ahmedabad
129 Atomic Energy Commission is located at Mumbai
130 Dynamics is the study of Movements of bodies
131 Statics is the study of Forces acting on bodies at rest
132 Mechanics is the study of Forces acting on bodies
133 Zoology is the study of Animal life
134 Botany is the study of Plant life
135 Psychology is the study of Human mind
136 The first American to orbit earth was John H.Glen
137 The electro-cardiograph was invented by William Einthoven
138 The molecular formula of cane sugar is C12H22O11
139 A compound which contains only hydrogen and Carbon is called a Hydrocarbon
140 The liquid used to preserve specimens of plans and animals is Formalin
141 The law of segregaton was propounded by Mendel
142 Auriscope is used to detect Ear disorders
143 The three states of matter are Solid,liquid and gas
144 The scientific name for blood platelets is Thrombocytes
145 The response of a plant to heat is called Thermotropism
146 The response of a plant to touch is called Trigmotropism
147 The symbol Zr stands for Zirconium
148 Nickel was discovered by Cronstledt
149 Manganese was discovered by Gahn
150 The common name for pottasium carbonate is Potash
151 Bismuth was discovered by Valentine
152 The biggest plant seed is Cocodemer
153 Toxicology is the study of Poisons
154 Virology is the study of Viruses
155 Paleontology is the study of Fossils
156 Calorimeter is used to measure Quantity of heat
157 Chronometer was invented by John Harrison
158 Stethoscope was invented by William Stockes
159 Spinning frame was invented by Sir Richard Arkwright
160 Al stands for Aluminium
161 Gd stands for Gadolinium
162 Ir stands for Iridium
163 Bi stands for Bismuth
164 The Chemical formula of sodium bicarbonate is NaHCO3
165 The chemical formula of common salt is Nacl
166 The chemical formula of washing soda is Na2CO3,IOH2O
167 The chemical formula of lime soda is CaCO3
168 The chemical formula of chloroform is CHcl3
169 The study of grasses is known as Agrostology
170 The study of antiquities is known as Archaeology
171 The study of the duration of life is known as Chronobiology
172 The study of bacteria is known as Bacteriology
173 Nylon was invented by Dr.Wallace H.Carothers
174 Electric razor was invented by Jacob Schick
175 The symbol of silver is Ag
176 The symbol of silicon is Si
177 The symbol of titanium is Ti
178 Calcium oxide is commonly known as Quick lime
179 A deviation of light passing from one medium to another is known as Refraction
180 An apparatus for generation of atomic energy is called a Reactor
181 A machine used for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy is called a Generator
182 The first Indian woman in space was Kalpana Chawla
183 The revolver was invented by Samuel Colt
184 The refrigerator was invented by J.Perkins
01 The theory of relativity was propounded by Albert Einstein
02 The principal metal used in manufacturing steel is Iron
03 An altimeter is used for measuring Altitude
04 Oology is the study of Birds eggs
05 Radioactivity was discovered by Henry Bacquerel
06 The metal used in storage batteries is Lead
07 The instrument used to measure the relative humidity of air is Hygrometer
08 Barometer was invented by Torricelli
09 The unit of power is Watt
10 Radium was discovered by Marie and Pierrie Curie
11 The existence of isotopes was discovered by Frederick Soddy
12 Dynamo was invented by Michael Faraday
13 The nuclear reactor was invented by Enrico Ferni
14 The law of gravitation was propounded by Sir Isaac Newton
15 Crescograph was invented by J.C.Bose
16 Crescograph is used to measure the Rate of growth of a plant
17 Galileo's first scientific discovery was Pendulum
18 Microscope was invented by Aaton Van Leewen Hock
19 The scientist who is known as father of modern biology is Aristotle
20 The first person to see a cell under microscope was Robert Hooke
21 The smallest flowering plant is Worffia
22 The four blood groups were discovered by Karl Landsteiner
23 Sodium was discovered by Sir Humphry Davy
24 The atomic number of oxygen is Eight
25 The basic building blocks of proteins are Amino acids
26 The botanical name of the cotton plant is Gossipium Hirsutum
27 An Electroscope is used to Detect charges on a body
28 The unit of loudness is Phon
29 An ammeter is used to measure Electric current
30 Plant that eat insects are called Insectivorous plants
31 Fruits that are formed without fertilization are called Parthenocarpic
32 Plants that flower only once in their lifetime are called Mono carpic
33 The botanical name for rice is Oryza Sativa
34 Penicillin is obtained from Mould
35 The largest tree in the world is Seguoia Gigantica
36 Herpetology is the study of Reptiles
37 Entomology is the study of Insects
38 Ornithology is the study of Birds
39 Ichtyology is the study of Fishes
40 Osteology is the study of Bones
41 The botanical name for brinjal is Solanum melongenal
42 The botanical name for onion is Allium Cepa
43 The study of sound is called Acoustics
44 The study of heavenly bodies is called Astronomy
45 The study of tissues is called Histology
46 Electric Lamp was invented by Thomas alva Edison
47 The fear of crowd is called Ochlophobia
48 The fear of books is called Bibliophobia
49 The fear of going to bed is called Clinophobia
50 The symbol of gold is Au
51 The symbol of sodium is Na
52 The symbol of Sr stands for Strontium
53 The symbol Rb stands for Rubidium
54 The symbol Md stands for Mendelevium
55 Calcium sulphate is commonly called Plaster of Paris
56 Sodium carbonate is commonly called Washing Soda
57 Sodium chloride is commonly known as Common Salt
58 The chemical name of Chloroform is Trichloromethane
59 The chemical name of baking powder is Sodium bicarbonate
60 The chemical name of bleaching powder is Calcium hypochlorite
61 The formula HCL stands for Hydrochloric Acid
62 The formula H2SO4 stands for Sulphuric Acid
63 The formula CHCI3 stands for Trichloromethane
64 The formula H2O2 stands for Hydrogen peroxide
65 A fungus which can only survive on other living organisms is called Obligate Parasite
66 A plant which lives in the dark is called Scotophyte
67 A plant adapted to live in dry places is called a Xerophyte
68 A plant adapted for growth in water is called a Hydrophyte
69 Bifocal lens was invented by Benjamin Franklin
70 Cement was invented by Joseph Aspdin
71 Laser was invented by Dr.Charles H.Townes
72 Electromagnet was invented by William Sturgeon
73 Rayon was invented by Sir Joseph Swann
74 Thermostat is an instrument used for regulating Constant temperature
75 The science of organic forms and structures is known as Morphology
76 Phycology is the study of Algae
77 Tata Institute of Fundamental Research was established in 1945
78 CSIR stands for Council of Scientific and Industrial Research
79 ISRO stands for Indian Space Research Organisation
80 The first human being to land on moon was Neil Armstrong
81 The first Indian in space was Rakesh Sharma
82 ISAC stands for ISRO Satellite Centre
83 VSSC stands for Vikram Sarabhai space Centre
84 The headquarters of ISRO is located at Bangalore
85 VSSC is located at Thiruvananthapuram
86 ISAC is located at Bangalore
87 National Science Centre is located at New Delhi
88 Central Tobacco Research Institute is located at Rajahmundry
89 Indian Institute of Horticultural Research is located at Bangalore
90 The Atomic Energy Commission was set up in August 1948
91 The first Indian Satellite was Aryabhatta
92 The first Indian Satellite was launched in the year 1975
93 ASLV stands for Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle
94 INSAT stands for Indian National Satellite
95 The fear of women is known as Gynophobia
96 The fear of men is known as Androphobia
97 The scientist who developed the Quantum theory was Max Plonck
98 The steam engine was invented by James Watt
99 The botanical name of tea is Camellia Sinensis
100 Logarithms were devised by John Napier
101 The acid used in a car battery is Sulphuric acid
102 The system for writing by blind people was invented by Louis Braille
103 The parachute was used for the first time by J.P.Blanchard
104 The German physicit who first demonstrated the existence of Radio waves was Henrich Hertz
105 The instrument that records the intensity of earthquakes is Seismograph
106 The laws of floating bodies was discovered by Archimedes
107 The density of milk is measured by a Lactometer
108 Fountain pen was invented by L.E.Waterman
109 The instrument used to measure the pressure of gases is the Monometer
110 Bhaskara I was a famous Astronomer
111 The first atomic power station established in India was the Tarapore Atomic Power Station
112 The role of heredity was demonstrated by Mendel
113 The instrument used to measure the concentration of salt water is the Salinometer
114 Spectroscopy is the study of Anders John Angstrom
115 Dactylography is the study of Finger Prints
116 A tangent galvanometer is used to study the Strength of direct current
117 The fruit of Oak is called Acron
118 ZETA stands for Zero Energy Thermonuclear Assembly
119 The formula C6H5OH stands for Phenol
120 Michael Faraday worked as an assistant under another scientist whose name was Sir Humphry Davy
121 Vulcanised rubber was invented by Charles Goodyear
122 The symbol Zn stands for Zinc
123 The symbol He stands for Helium
124 Celluloid was invented by A.Parker
125 Glider was invented by Sir George Caley
126 Safety matches was invented by J.E.Lundstrom
127 Radio valve was invented by Sir J.A.Fleming
128 Space Applications Centre is located at Ahmedabad
129 Atomic Energy Commission is located at Mumbai
130 Dynamics is the study of Movements of bodies
131 Statics is the study of Forces acting on bodies at rest
132 Mechanics is the study of Forces acting on bodies
133 Zoology is the study of Animal life
134 Botany is the study of Plant life
135 Psychology is the study of Human mind
136 The first American to orbit earth was John H.Glen
137 The electro-cardiograph was invented by William Einthoven
138 The molecular formula of cane sugar is C12H22O11
139 A compound which contains only hydrogen and Carbon is called a Hydrocarbon
140 The liquid used to preserve specimens of plans and animals is Formalin
141 The law of segregaton was propounded by Mendel
142 Auriscope is used to detect Ear disorders
143 The three states of matter are Solid,liquid and gas
144 The scientific name for blood platelets is Thrombocytes
145 The response of a plant to heat is called Thermotropism
146 The response of a plant to touch is called Trigmotropism
147 The symbol Zr stands for Zirconium
148 Nickel was discovered by Cronstledt
149 Manganese was discovered by Gahn
150 The common name for pottasium carbonate is Potash
151 Bismuth was discovered by Valentine
152 The biggest plant seed is Cocodemer
153 Toxicology is the study of Poisons
154 Virology is the study of Viruses
155 Paleontology is the study of Fossils
156 Calorimeter is used to measure Quantity of heat
157 Chronometer was invented by John Harrison
158 Stethoscope was invented by William Stockes
159 Spinning frame was invented by Sir Richard Arkwright
160 Al stands for Aluminium
161 Gd stands for Gadolinium
162 Ir stands for Iridium
163 Bi stands for Bismuth
164 The Chemical formula of sodium bicarbonate is NaHCO3
165 The chemical formula of common salt is Nacl
166 The chemical formula of washing soda is Na2CO3,IOH2O
167 The chemical formula of lime soda is CaCO3
168 The chemical formula of chloroform is CHcl3
169 The study of grasses is known as Agrostology
170 The study of antiquities is known as Archaeology
171 The study of the duration of life is known as Chronobiology
172 The study of bacteria is known as Bacteriology
173 Nylon was invented by Dr.Wallace H.Carothers
174 Electric razor was invented by Jacob Schick
175 The symbol of silver is Ag
176 The symbol of silicon is Si
177 The symbol of titanium is Ti
178 Calcium oxide is commonly known as Quick lime
179 A deviation of light passing from one medium to another is known as Refraction
180 An apparatus for generation of atomic energy is called a Reactor
181 A machine used for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy is called a Generator
182 The first Indian woman in space was Kalpana Chawla
183 The revolver was invented by Samuel Colt
184 The refrigerator was invented by J.Perkins
General Knowledge (GK) Page:20 --By: Vinod Kumar Dhundhara
1.
जिप्सम राजस्थान में सर्वाधिक कहां पर पाया जाता है।
- नागौर
2. राजस्थान में चांदी की खान कहां पर स्थित है।
- जावर (उदयपुर), रामपुरा-आंगुचा (भीलवाड़ा)
3. मैंगनीज राजस्थान के किस जिलों में पाया जाता है।
- बांसवाड़ा व उदयपुर
4. वरमीक्यूलाइट राजस्थान में कहां पर पाया जाता है।
- अजमेर
5. राजस्थान में मैग्नेसाइट कहां पर उत्पादित किया जाता है।
- अजमेर
6. राजस्थान में वोलस्टोनाइट कहां पाया जाता है।
- सिरोही व डूंगरपुर
7. यूरेनियम राजस्थान में कहां पर पाया जाता है।
- उदयपुर, डूंगरपुर, बांसवाड़ा व सीकर
8. अभ्रक राजस्थान में सर्वाधिक कहां पर पाया जाता है।
- भीलवाड़ा व उदयपुर
9. सीसा-जस्ता उत्पादन में राजस्थान का देश में कौनसा स्थान है।
- प्रथम
10. रॉक फास्फेट के राजस्थान में प्रमुख स्थान कौनसे हैं।
- झामर कोटड़ा (उदयपुर) व बिरमानियां (जैसलमेर)
11. मुल्तानी मिट्टी राजस्थान में कहां पाई जाती है।
- बीकानेर व बाड़मेर
12. पाइराइट्स राजस्थान में सर्वाधिक कहां पाया जाता है।
- सलादीपुर (सीकर)
13. राजस्थान में बेराइट्स के विशाल भंडार कहां पाये गए हैं।
- जगतपुर (उदयपुर)
14. घीया पत्थर राजस्थान में कहां पाया जाता है।
- भीलवाड़ा व उदयपुर
15. राजस्थान में कैल्साइट कहां पाया जाता है।
- सीकर व उदयपुर
16. केन्द्रीय स्वास्थ्य मंत्री कौन हैं?
- गुलाम नबी आजाद
17. केन्द्रीय जल संसाधन मंत्री कौन हैं? .
-पवन कुमार बंसल
18. संसद भवन का शुभारं किसने व कब किया ?
- 18 जनवरी 1927, लार्ड इरविन
19. राष्ट्रीय गणित दिवस कब मनाया जाएगा?
- 22 दिसंबर
20. राष्ट्रीय गणित वर्ष किस वर्ष को घोषित किया है।
- वर्ष 2012
- नागौर
2. राजस्थान में चांदी की खान कहां पर स्थित है।
- जावर (उदयपुर), रामपुरा-आंगुचा (भीलवाड़ा)
3. मैंगनीज राजस्थान के किस जिलों में पाया जाता है।
- बांसवाड़ा व उदयपुर
4. वरमीक्यूलाइट राजस्थान में कहां पर पाया जाता है।
- अजमेर
5. राजस्थान में मैग्नेसाइट कहां पर उत्पादित किया जाता है।
- अजमेर
6. राजस्थान में वोलस्टोनाइट कहां पाया जाता है।
- सिरोही व डूंगरपुर
7. यूरेनियम राजस्थान में कहां पर पाया जाता है।
- उदयपुर, डूंगरपुर, बांसवाड़ा व सीकर
8. अभ्रक राजस्थान में सर्वाधिक कहां पर पाया जाता है।
- भीलवाड़ा व उदयपुर
9. सीसा-जस्ता उत्पादन में राजस्थान का देश में कौनसा स्थान है।
- प्रथम
10. रॉक फास्फेट के राजस्थान में प्रमुख स्थान कौनसे हैं।
- झामर कोटड़ा (उदयपुर) व बिरमानियां (जैसलमेर)
11. मुल्तानी मिट्टी राजस्थान में कहां पाई जाती है।
- बीकानेर व बाड़मेर
12. पाइराइट्स राजस्थान में सर्वाधिक कहां पाया जाता है।
- सलादीपुर (सीकर)
13. राजस्थान में बेराइट्स के विशाल भंडार कहां पाये गए हैं।
- जगतपुर (उदयपुर)
14. घीया पत्थर राजस्थान में कहां पाया जाता है।
- भीलवाड़ा व उदयपुर
15. राजस्थान में कैल्साइट कहां पाया जाता है।
- सीकर व उदयपुर
16. केन्द्रीय स्वास्थ्य मंत्री कौन हैं?
- गुलाम नबी आजाद
17. केन्द्रीय जल संसाधन मंत्री कौन हैं? .
-पवन कुमार बंसल
18. संसद भवन का शुभारं किसने व कब किया ?
- 18 जनवरी 1927, लार्ड इरविन
19. राष्ट्रीय गणित दिवस कब मनाया जाएगा?
- 22 दिसंबर
20. राष्ट्रीय गणित वर्ष किस वर्ष को घोषित किया है।
- वर्ष 2012
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)









